Sexually transmitted infections (IST) can lead to more than just a difficult conversation with your last flight.
Research suggests that some STIs can increase your chances of developing dementia, a disease that concerns the memory that affects one in 10 seniors in the US
This is worrying, given that IST are blooming across the country, with more than 2.4 million cases reported only in 2023. Even more worrying, infections in adults aged 65 and older have doubled over the past decade.
With research showing that elderly adults are less likely to take regular emergence of IST and many health care providers who neglected to discuss sexual health with these patients, the age group may be particularly susceptible to long -term effects such as cognitive decline.
Here are four ISTs that can increase your chances of developing dementia.
shingles
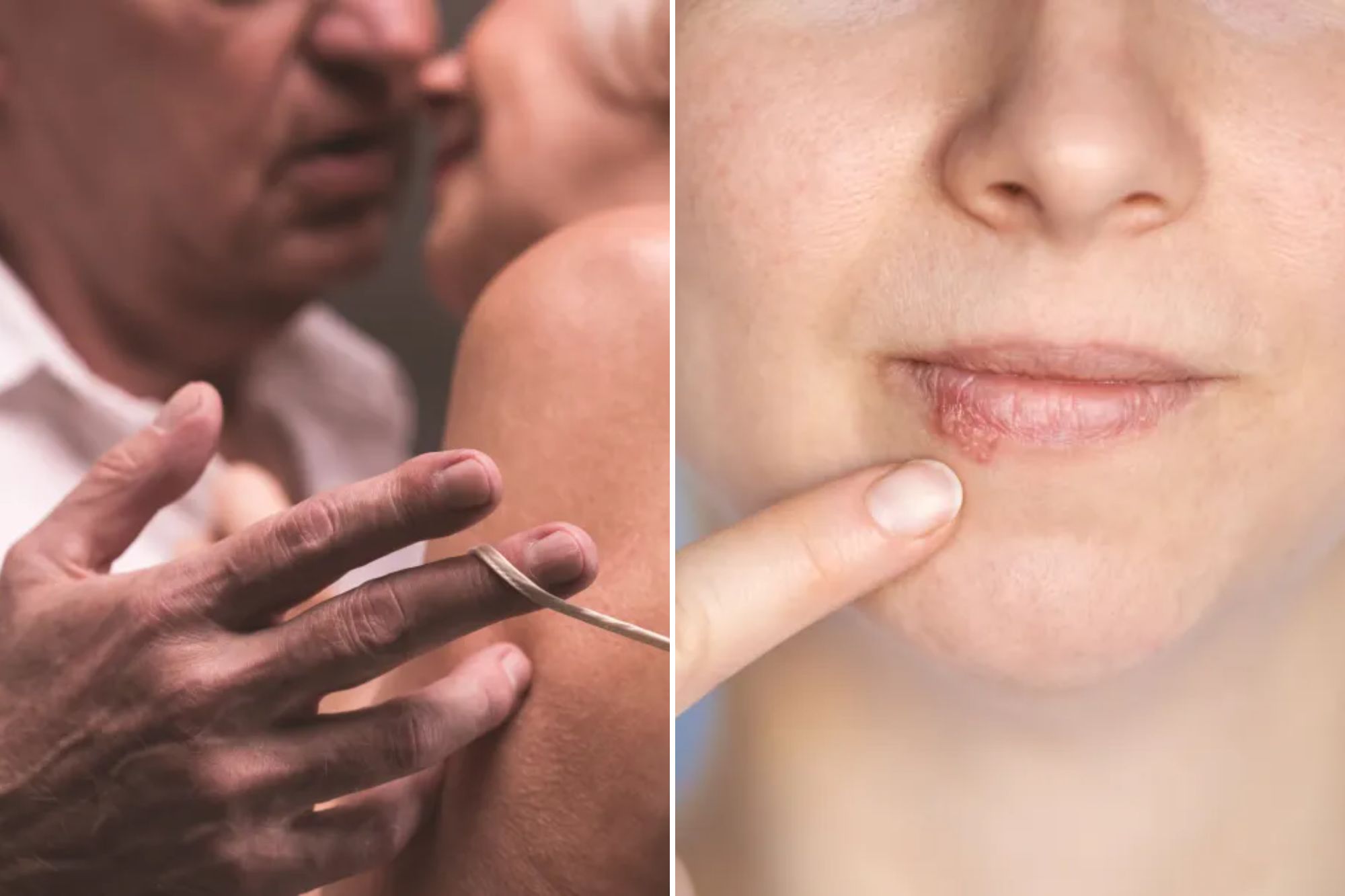
If you thought herpes was just a case of cold cold wounds, think again.
Between 50% and 80% of Americans have oral herpes (HSV-1), and 1 in 6 people aged 14 to 49 in JBA have genital herpes (HSV-2), according to Johns Hopkins.
But here is Kicker: the virus responsible for herpes can enter the brain and lie dormant, just to reactivate later. When occurs, some studies suggest that it can cause inflammation in the brain, potentially damaging brain cells and increasing the risk of dementia.
In fact, people with HSV-1, HSV-2, or both, have up to 2.44 times more likely to develop dementia than those who have never been infected, according to a 2024 study by the University of Texas medical branch.
“These findings underline the need for more research on mechanisms that underline the contribution of HSV to the cognitive decline and if such mechanisms can be aimed as a preventive strategy against dementia,” said Dr. Giulio Taglialatela, senior author and director of the UTMB Institute of Brain Health.
Siege
Siphilis is making a huge return to the US, and will not only touch the newest crowd: cases between adults aged 55 and older have increased by nearly 700% since 2010.â
While syphilis is treatable with penicillin and other antibiotics, if not addressed, the infection can affect any organ system. A particularly serious complication is neurosfilis, where bacteria invade the brain and spinal cord, causing inflammation and damage to the brain tissue.
In its subsequent stages, neurosfilis can lead to syphilitic dementia, which usually develops 10-25 years after initial infection. Symptoms include memory loss, confusion, personality changes, problems concentration, depression and even fraud.
The good news? Experts say neurosfilis -related madness is “potentially reversible”, but only if it is caught and treated early.
Genitals
CDC estimates that about 400,000 people in the US are living with genital warts at any given time.
Genital warts are a common IST caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV can contribute to brain inflammation, a major factor in the development of dementia.
A 2020 study using health insurance data from 16,000 patients in Taiwan found that individuals with HPV genital warts had an increased risk of 49% of the development of dementia. Research also shows that cervical cancer, associated with HPV, is associated with an increased risk of dementia.
Fortunately, the HPV vaccine protects against the strains responsible for most genital warts, and is very effective in preventing genital warts and cervical cancer.
HIV/AIDS
Nearly 1.2 million people in SH.BA are living with HIV.
When the virus spreads to the brain, it causes inflammation, damages brain cells and releases harmful toxins-all of these contribute to cognitive decline and, in severe cases, can lead to HIV-related dementia.
In a 2022 study, researchers compared 13,000 permanent HIV patients with over 155,000 people without a virus. They found that 2.5% of those with HIV were diagnosed with dementia over a 16-year-old conveyor period, compared to only 1.3% of those without.
On average, people with HIV were diagnosed with dementia 10 years ago than those without illness.
â € Reedics effective medicines have turned HIV into a manageable state for most patients, – said Dr. Jennifer Lam, a research scientist for the permanent Kaiser search division who conducted the study. “That is why it is important to address the health concerns that come with aging.
#Ist #increase #risk #dementia #growing #nursing #homes
Image Source : nypost.com